Reimagining Design Systems at Spotify
Discover what motivated us to create our new design system, how it’s structured, and how it’s different from what we’ve tried before.

Cronmaster: Self-Hosted Cron Control with a Clean UI
A tidy, practical web UI for managing host cron jobs and runnable scripts built with Next.js TypeScript and Tailwind and packaged to run from Docker for quick deployment.
(20+) Is Frontend Dead? The Evolution You Can't Ignore | daily.dev
Frontend development has evolved from simple UI work into full-system engineering. Modern frameworks like Next.js blur client-server boundaries with server components, edge deployment, and integrated data fetching. Developers now handle state management, security, performance optimization, and deployment—responsibilities traditionally split between frontend and backend roles. The shift demands understanding the complete user experience stack, from rendering strategies to authentication flows. This evolution creates opportunities for those who adapt by either broadening their skills across the full stack or specializing deeply in performance and user experience.
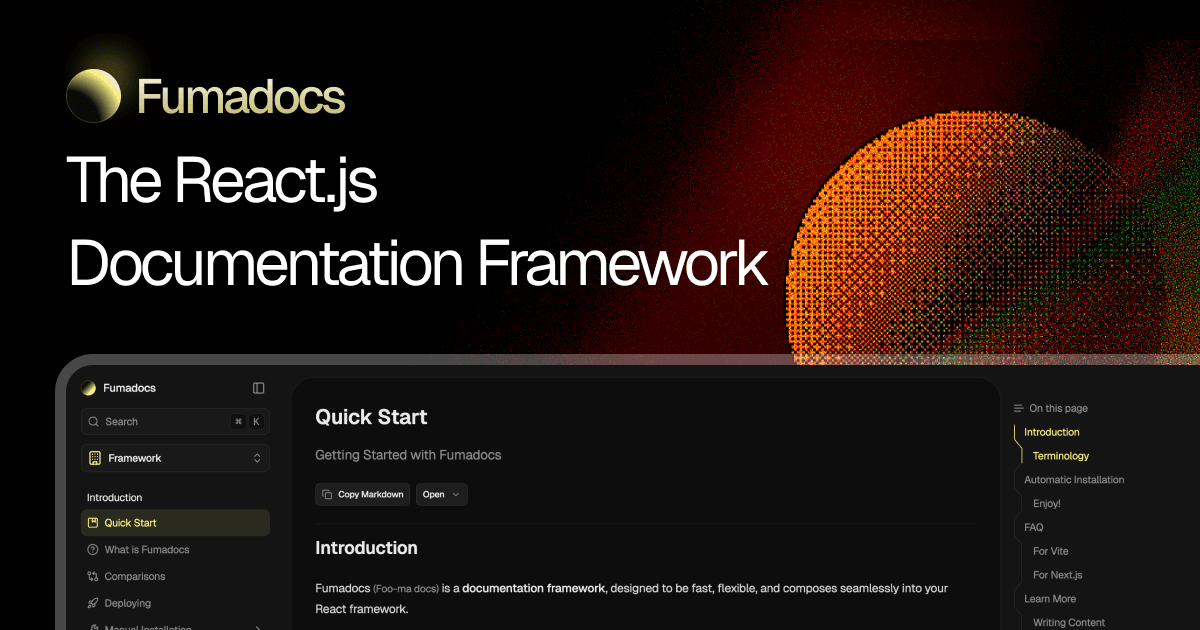
Fumadocs
The React.js documentation framework.
Randomized Text Effect | UI Layouts
A randomized text effect component for React that animates letters dynamically before revealing the final text. Perfect for creating suspenseful, futuristic, and engaging UI interactions. Available components: randomized-text-unveil.

Ahrefs—AI Marketing Platform Powered by Big Data
We help marketers drive visibility across AI search, SEO, content, and social – with the largest AI and search databases online.
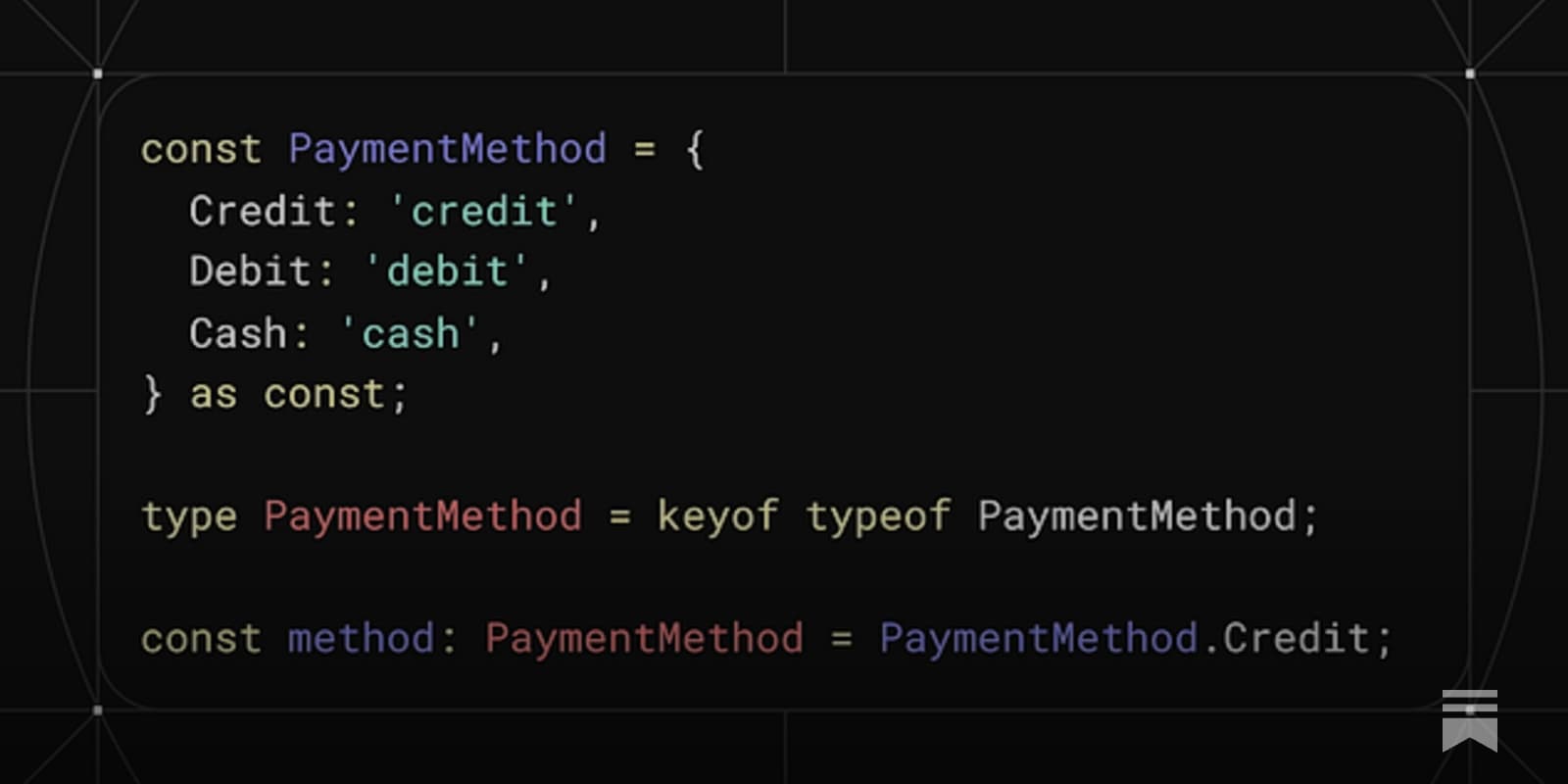
Shrink TypeScript Code: Replace Enums with Const Objects
A Smarter Way to Handle Enumerations in TypeScript

Careers - Langfuse
Join the Langfuse team to build the leading open-source LLM engineering platform

Functional Error Handling in Node.js With The Result Pattern
Learn how to improve your error handling in Node.js by using the Result Pattern. (5 Min)

How to Stand Out as a Developer in the AI Age
Why Context and Direction Matter More Than Typing Speed
Nedir bu Context Engineering ?
Prompt Engineering’i tam öğrenmişken nerden çıktı bu Context Engineering ?

How to Become a Machine Learning Engineer (Step-by-Step) | Towards Data Science
Your one-stop guide to becoming a machine learning engineer

uv cheatsheet
Cheatsheet with the most common and useful uv commands to manage projects and dependencies, publish projects, manage tools, and more.

11 System Design Concepts Explained, Simply
#88: Break Into System Design (9 Minutes)

Kibo UI
Kibo UI is a custom registry of composable, accessible and open source components designed for use with shadcn/ui.
Magic UI
Beautiful UI components and templates to make your landing page look stunning.

nuqs | Type-safe search params state management for React
Type-safe search params state management for React. Like useState, but stored in the URL query string.

ML Sistemleri Ders Kitabı
Açık Sosyal — aşırı tepki
The protocol is the API.

The world of programming has changed and with it the way to become a programmer
A programming language is no longer a destination, but represents only the first step of a path that has no end.
AI, Junior’ların Parlamasına Yardım Edecekti. Neden Asıl Senior’ları Daha Güçlü Hale Getiriyor? | Can ELMA/
AI junior geliştiricileri güçlendirecek deniyordu. Gerçekte ise senior’ları daha değerli hale getirip yazılım kültüründeki açıkları ortaya çıkardı.

How AI Vibe Coding Is Destroying Junior Developers' Careers
New research shows developers think AI makes them 20% faster but are actually 19% slower. Vibe coding is creating unemployable pseudo-developers who can't debug or maintain code.

9 advanced RAG techniques to know & how to implement them
Discover 9 key advanced RAG techniques and learn which tools can help you implement them.
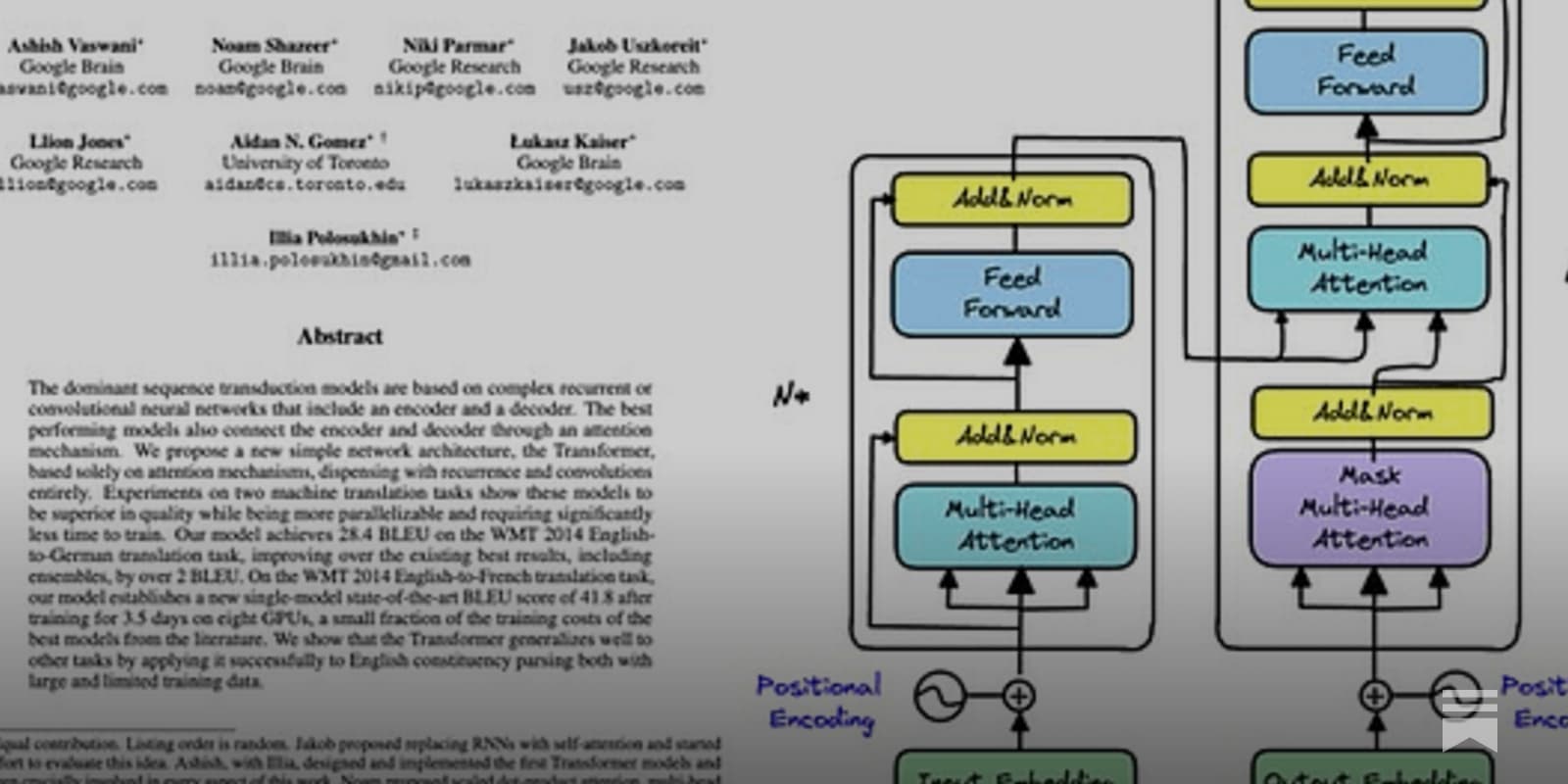
Implement "Attention is all you need"
...from scratch using PyTorch.
brew.mxkaske.dev
Never. Stop. Brewing.